Working with Different Git Accounts via SSH Configuration Using different git accounts can be simplified by setting up host aliases in the ~/. ssh/config file. This method will help you to separate the personal and professional repositories so that your Personal Access Token do not get mixed with GitHub account, as GitHub identifies accounts based on which SSH key for authentication are using to connect.
Understanding the Basics
In order to work with several accounts simultaneously two SSH keys must be created one is for your personal use and another for the faster. For instance, you can generate keys by following the command
textssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/. ssh/id_rsa_personal
ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/. ssh/id_rsa_work
Once you have created the keys add each public key to your GitHub account settings.
Configuring SSH Aliases
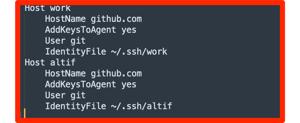
Next, modify your ~/. aliases in.ssh/config This approach allows you to provide the SSH Key that is going to be used when connecting into GitHub. A configuration may look like this:
textHost github-personal
HostName github.com
User git
IdentityFile ~/. ssh/id_rsa_personal
Host github-work
HostName github.com
User git
IdentityFile ~/. ssh/id_rsa_work
This way you can execute commands such as
textgit clone git@github-NAME:username/repo git
>
git clone git@github-work:username/repo git
This configuration will make sure that the right SSH key is used for separate accounts.multiple git accounts (ad)
Benefits of using SSH configurations
Lack of confusion: you know what to push/pull and from where
Security: Each account has a key to access it; preventing any shared credentials.
Switch to your accounts with few or no reconfigurations and fewer logins.
All in all, you can see that managing multiple git account with free CI/CD becomes very easy by following the above steps and this way they focus on developing only not at setting it up.