Deinococcus radiodurans is a particularly well studied bacterium due to its extreme resistance to radiation.
The bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans, which is commonly known as “Conan the Bacterium,” can resist high levels of ionizing radiation, but was only just beginning to be studied. This bacterium can withstand more than 100 double-strand breaks in its DNA without experiencing lethal or mutagenic effects unlike many other organisms. Its amazing DNA repair capabilities are weave around the biological nuts and bolts.
Mechanisms of DNA Repair
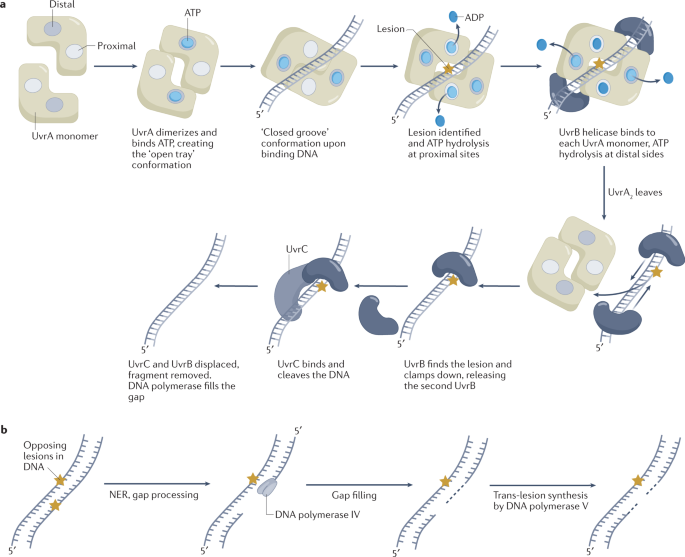
D. radiodurans uses multiple layers of DNA repair mechanisms, with major emphasis on homologous recombination and excision repair . RecA protein is critical for promoting homologous recombination, necessary to repair double-strand breaks accurately. Moreover, there are two separate but concerted DNA damage repair systems that work together to restore UV terrorism, which represents the great plurality in DNA damageresponse pattern of this species 13.
Biological Consequences and Application
The strength of D.radiation-resistance (ad) radiodurans has broad implications for several fields, including astrobiology and medicine. Insight into its DNA repair mechanisms may enable the creation of engineered strains for survival under extreme conditions on Earth or in space. In addition, knowledge learnt from research on this bacterium could be applied to clinical health strategies seeking to increase DNA repair in human cells — improving treatments for radiation-induced injuries or diseases that rely on precise DNA recreations 25.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Deinococcus radiodurans is a prime example of the clever ways nature has evolved to cope with extreme conditions and repair DNA. This analysis improves our insight not only into the resilience of microorganisms but also provides a basis and landmarks for future innovations in biotechnology aimed at survival in extreme habitats.