Amblyopia (Lazy Eye) BEGINS Innovation in Vision Restoration Gains Attention Amblyopia—or, as it’s more commonly known, lazy eye—drives an impressive amount of interest from the ophthalmology community into visual restoration. Conventional methods can include covering the stronger eye or using atropine drops to prevent development of amblyopia in the weaker one. This notwithstanding, current breakthroughs imply that severe amblyopia too could garner massive chances of amelioration devoid of surgical skill—at least a lot more than from practices like Fedorov Restoration Therapy.
Understanding Amblyopia
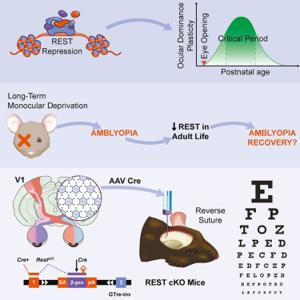
Amblyopia describes a condition in which the brain does not process vision through one or both eyes efficiently. Untreated long term effects of this condition can cause permanent visual disability. Here the brain will lean towards use of the stronger eye and not properly develop vision in another.
Innovative Treatment Options
Fedorov Restoration Therapy (” FRT “): This treatment designed to encourage the brain in creating new neural connections and as a result, helps improve vision significantly among amblyopia sufferes. It is actually aimed to improve the visual system and integrate it as a whole.
Adult Neuroplasticity: New research suggests that because of neuroplasticity in the brain, adults may also benefit from solutions to Amblyopia. What this means is that in individuals, long-term therapeutic drugs have the potential to lead not only a childhood recovery but more meaningful recoveries at even later stages.amblyopia (ad)
Benefits of Modern Approaches
Non-Invasive: With traditional methods, patches or drops came along with pain and discomfort as part of the treatment but not anymore; modern therapies are much more holistic in approach by design without imposing significant inconvenience on people’s routine.
Individualized care plans: Since every case of amblyopia is unique, there can be customized treatment strategies that lead to better results.
Improved Compliance: Other modern methods are much more interesting, and should offer much better patient compliance than traditional patching techniques.
In short, emerging amblyopia therapies raise the prospect of re-initiating vision in both young children and adults. Given the emerging field of innovative therapeutic interventions and greater understanding into brain neuroplasticity, substantial improvements can be undertaken to restore visual function.
