The brain and limited regenerative ability The brain is a high-complexity organ that has only a minimal range in functional restoration due to its complex structure and sparsity of neural stem cells (NSCs). The liver can recover well after suffering an acute injury, and the same goes for most other organs or tissues like the skin, but unfortunately not so efficiently in the brain.
Challenges in Brain Repair
Neural Stem Cells Scarce: There are few NSCs in the adult brain, but these cells exhibit significant regenerative power. However, these cells are found in distinct niches including the subventricular zone and hippocampus that makes locality for mobilization and activation challenging after injury15.
Glial Scar Formation: If the brain has experienced tissue damage, a glial scar would form in the injured area.brain regeneration (ad) This type of scar prevents migration of inflammatory cells and new neurons, forming a physical gap which limits effective healing and regeneration24.
Incomplete Integration of Transplanted Cells: Even if NSCs are introduced via therapies, they often do not integrate into original neural networks. One of the obstacles that remains is the fact that only a small percentage of exogenous neurons establish functional connections with host neurons after transplantation, which circumvents some motor recovery limits36.
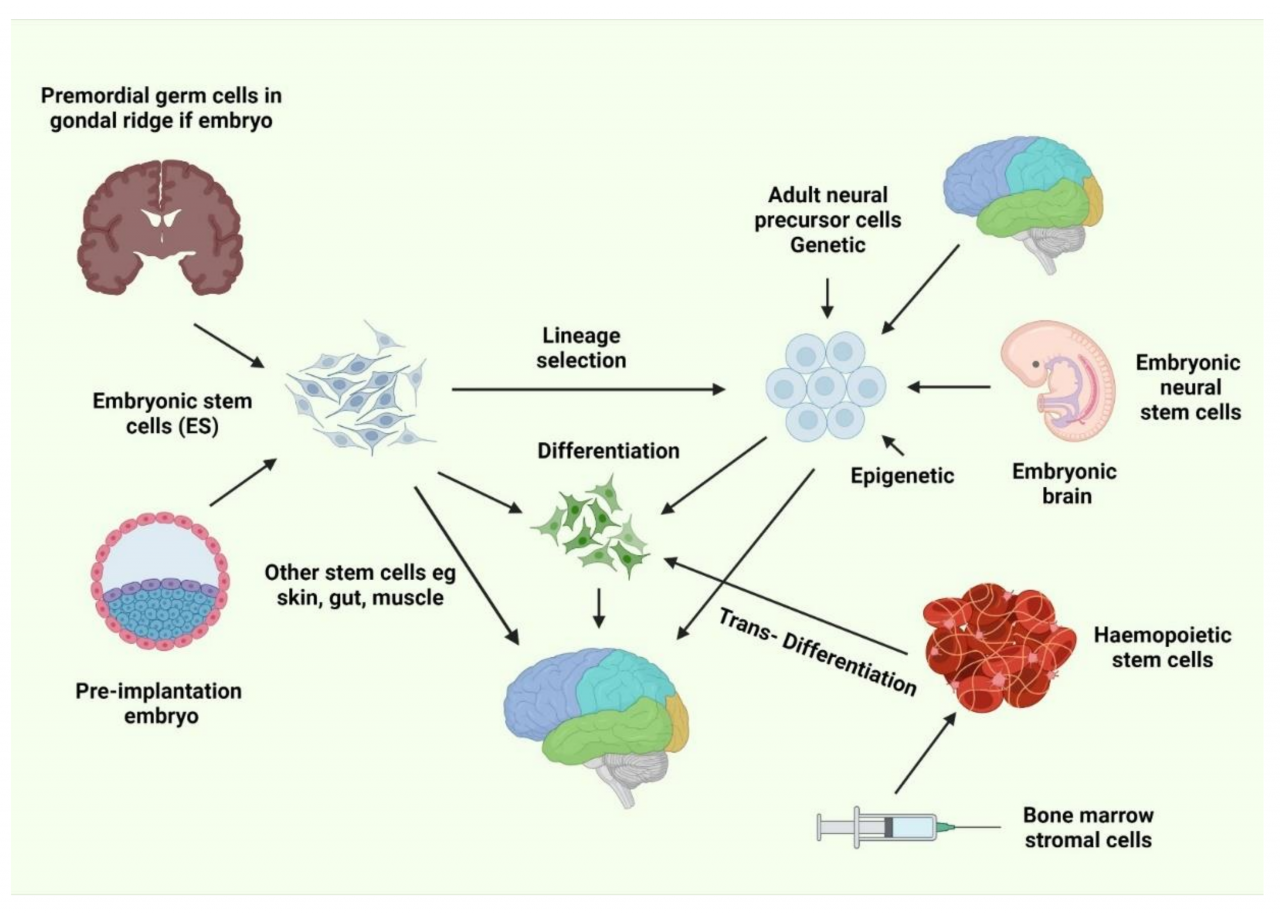
Current Research Directions
Stem Cell Therapies: Research is also directed toward improving the efficacy of NSC transplantation and to develop ways to activate endogenous stem cells to enhance recovery. Other innovative methods in experimental studies include the study of scaffolds for cells that are produced by bio-materials12.
Aspects of the stem cell niche Neurotrophic Factors — Scientists are also studying neurotrophic factors that can both preserve NSCs and induce differentiation of cells during treatment, which could increase therapeutic benefits in patients with brain injuries or neurodegenerative disease34.
Personalized Medicine Approaches: Other researchers are examining personalized stem cell therapies, in which patient cells can be reprogrammed into new neurons or glial cells56.
Taken together, although the brain is not as regenerative as other organs, there is hope that stem cell strategies and careful biomaterial design may be therapeutic following a head injury.