Mechanistic Techniques for Nerve Repair
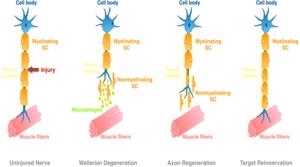
One of the biggest hurdles to recovery from nerve injuries is that they are incredibly slow and complicated for nerves. In cases of severed nerves, the nerve fibers follow a process that begins with retraction and cessation in activity for up to one month. Anniversary this interval, axons grow at 1 mm per era or in man terms an inch a month But what determines the depth of recovery is very particular to individual scenarios.
Variables that can affect nerve regeneration:
Miles to go: The more the miles between injury site and target organ, lesser becomes the chances for recovery. A reinnervation delays may cause muscle atrophy and other complications35.
Chronic Denervation: Exposure to nerve free intervals can lead to an inhibitory change in the distal environment for regenerating nerves. Other than Schwann cells becoming atrophic and less effective to support the re-growth of nerves after injury24.
Regenerative capacity: After a long period of denervation the neurons still have some regenerating capability, which is curious. There is more evidence that axons can reconnect if given an environment where they are able to grow back properly25.nerve regeneration (ad)
New Ways to Improve Recovery
Studies have concentrated on approaches to hastened up the regeneration of nerves. Among these are the conditioning electrical stimulation (CES) methods which showed promising outcomes to increase the regrowth rate by priming nerves for surgery 3. Furthermore, experimental approaches with growth factors and stem cell therapies are being tested to provide support for expanding axons13.
In conclusion, although two cut nerves may want to rejoin, the bonding of a severed nerve is subject to many biological and external factors. This information is important, because it aids researchers in developing therapies that could potentially advance the recovery of nerve injuries.
